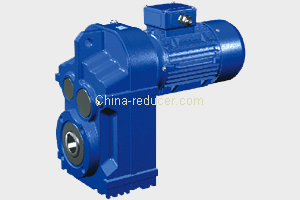
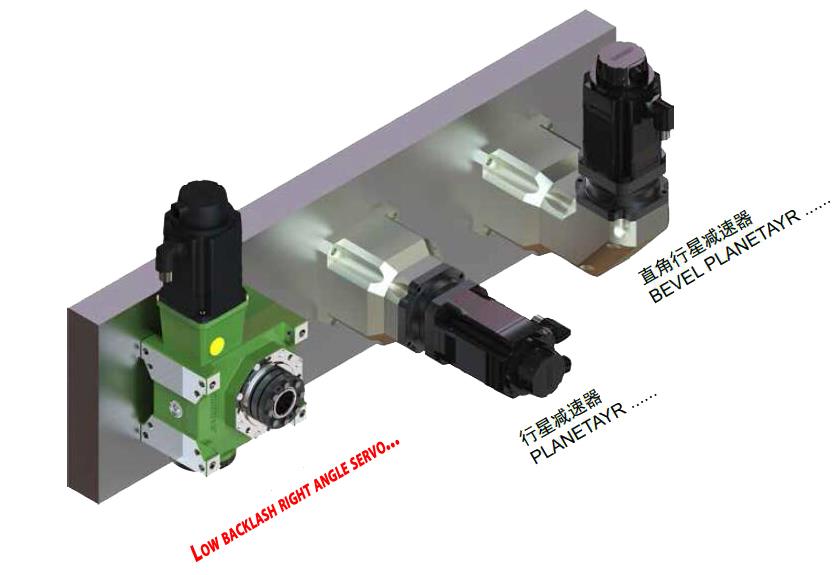
Low Backlash Right Angle Servo Worm Reducer
high precision worm gear is an ideal substitute for precision planetary gearbox,the equipment manufacturer can substantially reduce the cost of using precision planetary gearbox. The designer's ideal solution is to rotate 90 degrees to install the servo motor drive systems. Worm shaft in...

high precision worm gear is an ideal substitute for precision planetary gearbox,the equipment manufacturer can substantially reduce the cost of using precision planetary gearbox.
The designer's ideal solution is to rotate 90 degrees to install the servo motor drive systems.
Worm shaft in series can be driven by one motor to achieve synchronous output of multiple worm wheels. It has been used in automatic polishing mobile phone shell and other equipments
Servo worm gear units have three types : 45 - 50 - 55 - 63 - 75 - 90 ,with dual lead worm drive.Left and right flank of worm shaft using different lead angle,causing tooth thickness gradual change,So that you can move worm shaft and adjust backlash.
Low backlash Features :
-- Worm gear gyration backlash can be adjusted to less than 1 arc.
-- Reducer can be re-adjusted the gap after using .
-- Input with coupling : reliable without backlash .
-- Output using conical clamping ring couplings : reliable without backlash.
Applications :
Precision rotary motion
-- Reducing the noise and vibration that is caused by the load change and the change of cutting force.
-- reducing the noise and impact that is caused by the corotation and reverse.
-- By reducing worm abrasion.
-- Increasing worm output response speed .
Precision Indexing device
-- CNC machine, assembly line, cutting machine, transmission lines, etc.
-- Indexing device,accurate reading mechanism require accurate movement occasions .
Speed changing situations
-- Reducing the noise and the impact that is caused by speed change.
-- Reducing the worm abrasion that is caused by speed changes.
Low rotation Make choice :
The following headings contain information on essential elements for selection and correct use of gearbox.
For specific data on the gearbox range,see the relevant chapters.
OUTPUT TORQUE
1、Rated output torque
Mn2 [Nm]
The torque that can be transmitted continuously through the output shaft, with the gear unit operated under a service factor fs = 1.
2、Required torque
Mr2 [Nm]
The torque demand based on application requirement. It is recommended to be equal to or less than torque Mn2 the gearbox under study is rated for.
3、Calculated torque
Mc2 [Nm]
Computational torque value to be used when selecting the gearbox. It is calculated considering the required torque Mr2 and service factor fs, as per the relationship here after: POWER
POWER
1、Rated input power
Pn1 [kW]
The parameter can be found in the gearbox rating charts and represents the KW that can be safely transmitted to the gearbox, based on input speed n1 and service factor fs= 1.
2、Rated output power
Pn2 [kW]
This value is the power transmitted at gearbox output. it can be calculated with the following formulas: EFFICIENCY
EFFICIENCY
Efficiency is a parameter which has a major influence on the sizing of certain applications, and basically depends on gear pair designelements.
The mesh data table on page 9 shows dynamic efficiency (n1=1400)and static efficiency values.
Remember that these values are only achieved after the unit has been run in and is at the working temperature.
1、Dynamic efficiency
[ηd]
The dynamic efficiency is the relationship of power delivered at output shaft P2 to power applied at input shaft P1:
2、Static efficiency
[ηs]
Efficiency obtained at start-up of the gearbox. Although this is generally not significant factor for helical gears, it may be instead critical when selecting worm gearmotors operating under intermittent duty.
SERVICE FACTOR [ fs ]
The service factor (fs ) depends on the operating conditions the gearbox is subjected to the parameters that need to be taken into consideration to select the most adequate servies factor correctly comprise:
1. type of load of the operated machine : A - B - C
2. length of daily operating time: hours/day(△)
3. start-up frequency: starts/hour (*)
TYPE OF LOAD: A - uniform, fa≤0.3
B - moderate shocks, fa≤3
C - heavy shocks, fa≤10
fa=Je/Jm
--Je(kgm2) moment of the external inertia reduced at the drive shaft
--Jm(kgm2) moment of inertia of motor
--If fa>10 please contact our Technical Service
A -Screw feeders for light materials, fans, assembly lines, conveyor belts for light materials, small mixers, lifts, cleaning machines, fillers, control machines.
B -Winding devices, woodworking machine feeders, goods lifts, balancers,threading machines, medium mixers, conveyor belts for heavy materials,winches, sliding doors, fertilizer scrapers, packing machines, concrete mixers, crane mechanisms, milling cutters, folding machines, gear pumps.
C -Mixers for heavy materials, shears, presses, centrifuges, rotating supports, winches and lifts for heavy materials, grinding lathes, stone mills, bucket elevators, drilling machines, hammer mills, cam presses, folding machines, turntables, tumbling barrels, vibrators, shredders.











 Request a Brochure
and Samples
Request a Brochure
and Samples